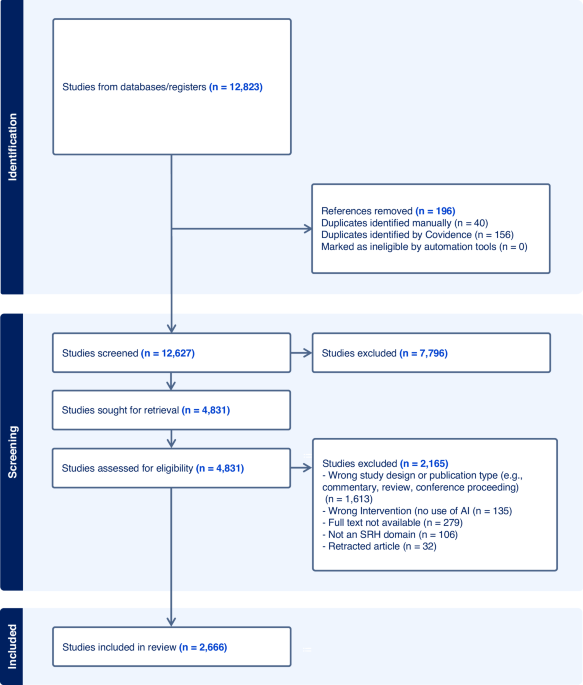
Okeibunor, J. C. et al. The use of artificial intelligence for delivery of essential health services across WHO regions: a scoping review. Front. Public Health 11, 1102185 (2023).
Google Scholar
World Health Organization. Regulatory Considerations on Artificial Intelligence for Health (World Health Organization, 2023).
Hernström, V. et al. Screening performance and characteristics of breast cancer detected in the Mammography Screening with Artificial Intelligence trial (MASAI): a randomised, controlled, parallel-group, non-inferiority, single-blinded, screening accuracy study. Lancet Digit. Health. (2025).
Kim, Y. H. Artificial intelligence in medical ultrasonography: driving on an unpaved road. Ultrasonography 40, 313–317 (2021).
Google Scholar
Esmaeilzadeh, P. Challenges and strategies for wide-scale artificial intelligence (AI) deployment in healthcare practices: a perspective for healthcare organizations. Artif. Intell. Med. 151, 102861 (2024).
Google Scholar
Locke, S. et al. Natural language processing in medicine: a review. Trends Anaesth. Crit. Care 38, 4–9 (2021).
Pujari, S. et al. Artificial intelligence for global health: cautious optimism with safeguards. Bull. World Health Organ. 101, 364–364a (2023).
Google Scholar
Rajpurkar, P., Chen, E., Banerjee, O. & Topol, E. J. AI in health and medicine. Nat. Med. 28, 31–38 (2022).
Google Scholar
Bauer, G. R. & Lizotte, D. J. Artificial intelligence, intersectionality, and the future of public health. Am. J. Public Health 111, 98–100 (2021).
Google Scholar
Benke, K. & Benke, G. Artificial intelligence and big data in public health. Int J. Environ. Res Public Health 15, 1–9 (2018).
Google Scholar
Bhatt, P., Liu, J., Gong, Y., Wang, J. & Guo, Y. Emerging artificial intelligence-empowered mhealth: scoping review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 10, e35053 (2022).
Google Scholar
Young, S. D., Crowley, J. S. & Vermund, S. H. Artificial intelligence and sexual health in the USA. Lancet Digit. Health 3, e467–e468 (2021).
Google Scholar
Saxena, A. K., Ness, S. & Khinvasara, T. The influence of AI: the revolutionary effects of artificial intelligence in healthcare sector. J. Eng. Res. Rep. 26, 49–62 (2024).
Google Scholar
Gbagbo, F. Y., Ameyaw, E. K. & Yaya, S. Artificial intelligence and sexual reproductive health and rights: a technological leap towards achieving sustainable development goal target 3.7. Reprod. Health 21, 196 (2024).
Google Scholar
Abou Chawareb, E. et al. Sexual health in the era of artificial intelligence: a review of the literature. J. Sex. Med. 21, 267–279 (2024).
Google Scholar
Wasson, E. J., Driver, K., Hughes, M. & Bailey, J. Sexual reproductive health chatbots: should we be so quick to throw artificial intelligence out with the bathwater?. BMJ Sex. Reprod. Health 47, 73 (2021).
Google Scholar
Mills, R., Mangone, E. R., Lesh, N., Mohan, D. & Baraitser, P. Chatbots to improve sexual and reproductive health: realist synthesis. J. Med. Internet. Res. 25, e46761 (2023).
Google Scholar
Delanerolle, G. et al. Artificial intelligence: a rapid case for advancement in the personalization of Gynaecology/Obstetric and Mental Health care. Women’s Health 17, 1–2 (2021).
Wang, R. et al. Artificial intelligence in reproductive medicine. Reproduction 158, R139–R154 (2019).
Google Scholar
Rolfes, V. et al. Artificial intelligence in reproductive medicine—an ethical perspective. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 83, 106–115 (2023).
Google Scholar
Buslón, N., Cortés, A., Catuara-Solarz, S., Cirillo, D. & Rementeria, M. J. Raising awareness of sex and gender bias in artificial intelligence and health. Front Glob. Women’s Health 4, 970312 (2023).
Google Scholar
World Health Organization. The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Sexual and Reproductive Health and Rights: Technical Brief (World Health Organization, 2024).
World Health Organization. Sexual and Reproductive Health Interventions in the WHO UHC Compendium (World Health Organization, 2021).
Khosla, R., Mishra, V. & Singh, S. Sexual and reproductive health and rights and bodily autonomy in a digital world. Sex. Reprod. Health Matters 31, 2269003 (2023).
Google Scholar
Chan, S. Y. et al. Computer-assisted image analysis of sperm concentration in human semen before and after swim-up separation: comparison with assessment by haemocytometer. Int. J. Androl. 12, 339–345 (1989).
Google Scholar
Bassil, H. E. & Dripps, J. H. Real time processing and analysis of fetal phonocardiographic signals. Clin. Phys. Physiol. Meas. 10, 67–74 (1989).
Google Scholar
Hu, H., Wang, H., Bai, Y. & Liu, M. Determination of endometrial carcinoma with gene expression based on optimized Elman neural network. Appl. Math. Comput. 341, 204–214 (2019).
Boudet, S., Houzé de l’Aulnoit, A., Peyrodie, L., Demailly, R. & Houzé de l’Aulnoit, D. Use of deep learning to detect the maternal heart rate and false signals on fetal heart rate recordings. Biosensors. (2022).
Bano, S. et al. FetNet: a recurrent convolutional network for occlusion identification in fetoscopic videos. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radio. Surg. 15, 791–801 (2020).
Google Scholar
Potluri, V. et al. An inexpensive smartphone-based device for point-of-care ovulation testing. Lab Chip 19, 59–67 (2018).
Google Scholar
Orel, E. et al. Prediction of HIV status based on socio-behavioural characteristics in East and Southern Africa. PLoS ONE 17, e0264429 (2022).
Google Scholar
Fox, H., Topp, S. M., Lindsay, D. & Callander, E. A cascade of interventions: a classification tree analysis of the determinants of primary cesareans in Australian public hospitals. Birth 48, 209–220 (2021).
Google Scholar
Betts, K. S., Kisely, S. & Alati, R. Predicting common maternal postpartum complications: leveraging health administrative data and machine learning. Bjog 126, 702–709 (2019).
Google Scholar
Khanam, R. et al. Performance of a validated spontaneous preterm delivery predictor in South Asian and Sub-Saharan African women: a nested case control study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 35, 8878–8886 (2022).
Google Scholar
Jehan, F. et al. Multiomics characterization of preterm birth in low- and middle-income countries. JAMA Netw. Open 3, e2029655 (2020).
Google Scholar
Hossain, M. I. et al. Performance evaluation of machine learning algorithm for classification of unintended pregnancy among married women in Bangladesh. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 1460908 (2022).
Google Scholar
Boucher, J. C. et al. HPV vaccine narratives on Twitter during the COVID-19 pandemic: a social network, thematic, and sentiment analysis. BMC Public Health 23, 694 (2023).
Google Scholar
Du, J., Xu, J., Song, H. Y. & Tao, C. Leveraging machine learning-based approaches to assess human papillomavirus vaccination sentiment trends with Twitter data. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak. 17, 69 (2017).
Google Scholar
Luo, X., Zimet, G. & Shah, S. A natural language processing framework to analyse the opinions on HPV vaccination reflected in Twitter over 10 years (2008–2017). Hum. Vaccin Immunother. 15, 1496–1504 (2019).
Google Scholar
Valdez, D. & Goodson, P. Neutral or framed? A sentiment analysis of 2019 abortion laws. Sex. Res. Soc. Policy 19, 936–945 (2022).
Google Scholar
Fatima, I. et al. Prediction of postpartum depression using machine learning techniques from social media text. Expert Syst. 36, e12409 (2019).
Google Scholar
Chivers, B. R. et al. Perinatal distress during COVID-19: thematic analysis of an online parenting forum. J. Med. Internet. Res. 22, e22002 (2020).
Google Scholar
Ravaldi, C., Mosconi, L., Bonaiuti, R. & Vannacci, A. The emotional landscape of pregnancy and postpartum during the COVID-19 pandemic in Italy: a mixed-method analysis using artificial intelligence. J. Clin. Med. 12, 6140 (2023).
Google Scholar
Gardiner, P. et al. Using health information technology to engage African American women on nutrition and supplement use during the preconception period. Front Endocrinol. 11, 571705 (2020).
Google Scholar
Jack, B. et al. Reducing Preconception Risks Among African American Women with Conversational Agent Technology. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 28, 441–451 (2015).
Google Scholar
Bonnevie, E. et al. Layla’s Got You: developing a tailored contraception chatbot for Black and Hispanic young women. Health Educ. J. 80, 413–424 (2021).
Google Scholar
Peng, M. L. et al. Formative evaluation of the acceptance of HIV prevention artificial intelligence chatbots by men who have sex with men in Malaysia: focus group study. JMIR Form. Res. 6, e42055 (2022).
Google Scholar
Wang, H. et al. An artificial intelligence chatbot for young people’s sexual and reproductive health in India (SnehAI): instrumental case study. J. Med. Internet. Res. 24, e29969 (2022).
Google Scholar
Fragoulakis, V. et al. Follitropin Alpha for assisted reproduction: an analysis based on a non-interventional study in Greece. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 38, 2227–2235 (2022).
Google Scholar
Zang, X. et al. Prioritizing additional data collection to reduce decision uncertainty in the HIV/AIDS response in 6 US cities: a value of information analysis. Value Health 23, 1534–1542 (2020).
Google Scholar
Chen, Y. et al. Machine-learning predictive model of pregnancy-induced hypertension in the first trimester. Hypertension Res. 46, 2135–2144 (2023).
Google Scholar
Cubillos, G. et al. Development of machine learning models to predict gestational diabetes risk in the first half of pregnancy. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 23, 469 (2023).
Google Scholar
Liu, J. et al. Machine learning-based prediction of postpartum hemorrhage after vaginal delivery: combining bleeding high risk factors and uterine contraction curve. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 306, 1015–1025 (2022).
Google Scholar
Zhu, H. et al. A computerized diagnostic model for automatically evaluating placenta accrete spectrum disorders based on the combined MR radiomics-clinical signatures. Sci. Rep. 12, 10130 (2022).
Google Scholar
Chen, L., Tian, Y., Deng, Y. & Abdulhay, E. Neural network algorithm-based three-dimensional ultrasound evaluation in the diagnosis of fetal spina bifida. Sci. Program. 2021, 3605739 (2021).
Gong, Y. et al. Fetal congenital heart disease echocardiogram screening based on DGACNN: adversarial one-class classification combined with video transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 39, 1206–1222 (2020).
Google Scholar
Song, F. et al. Predicting the risk of fetal growth restriction by radiomics analysis of the placenta on T2WI: a retrospective case-control study. Placenta 134, 15–22 (2023).
Google Scholar
Miyagi, Y. & Miyake, T. Potential of artificial intelligence for estimating Japanese fetal weights. Acta Med Okayama. (2020).
Veerabhadrappa, S. T. & Vyas, A. L. Analysis and classification of three trimesters during normal pregnancy using bispectrum. IETE J. Res. 68, 2697–2706 (2022).
Google Scholar
Xiao, Y., Lu, Y., Liu, M., Zeng, R. & Bai, J. A deep feature fusion network for fetal state assessment. Front Physiol. 13, 969052 (2022).
Google Scholar
De Ramón Fernández, A., Ruiz Fernández, D. & Prieto Sánchez, M. T. Prediction of the mode of delivery using artificial intelligence algorithms. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 219, 106740 (2022).
Google Scholar
Guedalia, J. et al. Transporting an artificial intelligence model to predict emergency cesarean delivery: overcoming challenges posed by interfacility variation. J. Med. Internet. Res. 23, e28120 (2021).
Google Scholar
Yu, S., Tan, K. K., Sng, B. L., Li, S. & Sia, A. T. H. Lumbar ultrasound image feature extraction and classification with support vector machine. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 41, 2677–2689 (2015).
Google Scholar
Bodnar, L. M. et al. Machine learning as a strategy to account for dietary synergy: an illustration based on dietary intake and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 111, 1235–1243 (2020).
Google Scholar
Fang, H., Johnson, C., Stopp, C. & Espy, K. A. A new look at quantifying tobacco exposure during pregnancy using fuzzy clustering. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 33, 155–165 (2011).
Google Scholar
Li, Q. et al. Effect of airborne particulate matter of 2.5μm or less on preterm birth: a national birth cohort study in China. Environ. Int. 121, 1128–1136 (2018).
Google Scholar
Roh, M. E. et al. Association between indoor residual spraying and pregnancy outcomes: a quasi-experimental study from Uganda. Int. J. Epidemiol. 51, 1489–1501 (2022).
Google Scholar
Amit, G. et al. Estimation of postpartum depression risk from electronic health records using machine learning. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 21, 630 (2021).
Google Scholar
Betts, K. S., Kisely, S. & Alati, R. Predicting postpartum psychiatric admission using a machine learning approach. J. Psychiatr. Res. 130, 35–40 (2020).
Google Scholar
Fischbein, R., Cook, H. L., Baughman, K. & Díaz, S. R. Using machine learning to predict help-seeking among 2016–2018 Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System participants with postpartum depression symptoms. Women’s. Health 18, 17455057221139664 (2022).
Google Scholar
Gopalakrishnan, A., Venkataraman, R., Gururajan, R., Zhou, X. & Zhu, G. Predicting women with postpartum depression symptoms using machine learning techniques. Mathematics 10, 4570 (2022).
Google Scholar
Khapre, S., Stewart, R. & Taylor, C. An evaluation of symptom domains in the 2 years before pregnancy as predictors of relapse in the perinatal period in women with severe mental illness. Eur. Psychiatry 64, e26 (2021).
Google Scholar
Shatte, A. B. R., Hutchinson, D. M., Fuller-Tyszkiewicz, M. & Teague, S. J. Social media markers to identify fathers at risk of postpartum depression: a machine learning approach. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 23, 611–618 (2020).
Google Scholar
Zhang, Y., Wang, S., Hermann, A., Joly, R. & Pathak, J. Development and validation of a machine learning algorithm for predicting the risk of postpartum depression among pregnant women. J. Affect. Disord. 279, 1–8 (2021).
Google Scholar
Lu, Q. et al. Longitudinal metabolomics integrated with machine learning identifies novel biomarkers of gestational diabetes mellitus. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 209, 9–17 (2023).
Google Scholar
Eguchi, A., Sakurai, K., Watanabe, M. & Mori, C. Exploration of potential biomarkers and related biological pathways for PCB exposure in maternal and cord serum: a pilot birth cohort study in Chiba, Japan. Environ. Int. 102, 157–164 (2017).
Google Scholar
Demailly, R., Escolano, S., Haramburu, F., Tubert-Bitter, P. & Ahmed, I. Identifying drugs inducing prematurity by mining claims data with high-dimensional confounder score strategies. Drug Saf. 43, 549–559 (2020).
Google Scholar
Chen, S. et al. Association of the LEP gene with immune infiltration as a diagnostic biomarker in preeclampsia. Front. Mol. Biosci. (2023).
Jihong, C. et al. Automated intensity modulated radiation therapy treatment planning for cervical cancer based on convolution neural network. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 19, 1533033820957002 (2020).
Google Scholar
Ecker, S. et al. Neural network-assisted automated image registration for MRI-guided adaptive brachytherapy in cervical cancer. Z. Med. Phys. 32, 488–499 (2022).
Google Scholar
Chauhan, N. K., Singh, K., Kumar, A. & Kolambakar, S. B. HDFCN: a robust hybrid deep network based on feature concatenation for cervical cancer diagnosis on WSI pap smear slides. BioMed. Res. Int. 2023, 4214817 (2023).
Google Scholar
Bhuvaneshwari, K. & Poornima, B. Cervical cancer cell identification & detection using fuzzy C mean and K nearest neighbor techniques. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 8, 1080–1084 (2019).
Google Scholar
Lefebvre, T. L. et al. Development and validation of multiparametric MRI-based radiomics models for preoperative risk stratification of endometrial cancer. Radiology 305, 375–386 (2022).
Google Scholar
Moro, F. et al. Developing and validating ultrasound-based radiomics models for predicting high-risk endometrial cancer. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 60, 256–268 (2022).
Google Scholar
Ahmed, M. R., Rehana, H. & Asaduzzaman, S. Ovarian cancer substantial risk factor analysis by machine learning: a low incoming country perspective. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 11, 8457–8466 (2020).
Amarsee, K. et al. Automatic detection and tracking of marker seeds implanted in prostate cancer patients using a deep learning algorithm. J. Med. Phys. 46, 80–87 (2021).
Google Scholar
Grimley, P. M. et al. A prognostic system for epithelial ovarian carcinomas using machine learning. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 100, 1511–1519 (2021).
Google Scholar
Paik, E. S. et al. Prediction of survival outcomes in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer using machine learning methods. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 30, e65 (2019).
Ling, Y., Zhang, W., Li, Z., Pu, X. & Ren, Y. Application and comparison of several machine learning methods in the prognosis of cervical cancer. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 43, 34–44 (2022).
Maurya, S. et al. Morphological analysis of metabolically dysregulated spermatozoa using Artificial Intelligence based approach. J. Integr. Sci. Technol. 11, 569–569 (2023).
Aristoteles, A., Syarif, A., Sutyarso, S. & Lumbanraja, F. R. Identification of human sperm based on morphology using the you only look once version 4 algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 13, 424–431 (2022).
Hassan, M. R., Al-Insaif, S., Hossain, M. I. & Kamruzzaman, J. A machine learning approach for prediction of pregnancy outcome following IVF treatment. Neural Comput. Appl. 32, 2283–2297 (2020).
Google Scholar
Amini, P. et al. Factors associated with in vitro fertilization live birth outcome: a comparison of different classification methods. Int. J. Fertil. Steril. 15, 128 (2021).
Google Scholar
Huang, B. et al. Using deep learning to predict the outcome of live birth from more than 10,000 embryo data. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 22, 36 (2022).
Google Scholar
Uyar, A., Bener, A. & Ciray, H. N. Predictive modeling of implantation outcome in an in vitro fertilization setting: an application of machine learning methods. Med. Decis. Mak. 35, 714–725 (2015).
Google Scholar
Wang, R. et al. AI-Based Optimal Treatment Strategy Selection for Female Infertility for First and Subsequent IVF-ET Cycles. J. Med. Syst. 47, 87 (2023).
Google Scholar
Mehrjerd, A., Rezaei, H., Eslami, S., Ratna, M. B. & Khadem Ghaebi, N. Internal validation and comparison of predictive models to determine success rate of infertility treatments: a retrospective study of 2485 cycles. Sci. Rep. 12, 7216 (2022).
Google Scholar
Targosz, A., Przystałka, P., Wiaderkiewicz, R. & Mrugacz, G. Semantic segmentation of human oocyte images using deep neural networks. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 20, 40 (2021).
Google Scholar
Bormann, C. L. et al. Consistency and objectivity of automated embryo assessments using deep neural networks. Fertil. Steril. 113, 781–787.e781 (2020).
Google Scholar
Dirvanauskas, D., Maskeliunas, R., Raudonis, V. & Damasevicius, R. Embryo development stage prediction algorithm for automated time lapse incubators. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 177, 161–174 (2019).
Google Scholar
Wald, M. et al. Computational models for prediction of IVF/ICSI outcomes with surgically retrieved spermatozoa. Reprod. Biomed. Online 11, 325–331 (2005).
Google Scholar
Tian, T. et al. A Bayesian network model for prediction of low or failed fertilization in assisted reproductive technology based on a large clinical real-world data. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 21, 8 (2023).
Google Scholar
Hicks, S. A. et al. Machine learning-based analysis of sperm videos and participant data for male fertility prediction. Sci. Rep. 9, 16770 (2019).
Google Scholar
Li, M. et al. Evaluation of endometrial receptivity by ultrasound elastography to predict pregnancy outcome is a non-invasive and worthwhile method. Biotechnol. Genet Eng. Rev. 40, 284–298 (2024).
Google Scholar
Koesoema Wijaya, R. A., Kusumaatmaja, A. & Rizal, D. M. Novel method to classify varicocele using electronic nose. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 28, 165–173 (2022).
Mukherjee, G., Zhang, C., Kandaswamy, S., Gooding, H. & Orenstein, E. Current inpatient screening practices for sexual history and STIs: an opportunity to seize. Clin. Pediatr. 63, 350–356 (2024).
Google Scholar
Wray, T. B. et al. Using smartphone survey data and machine learning to identify situational and contextual risk factors for HIV risk behavior among men who have sex with men who are not on PrEP. Prev. Sci. 20, 904–913 (2019).
Google Scholar
Parra-Rodriguez, L. et al. Common antiretroviral combinations are associated with somatic depressive symptoms in women with HIV. AIDS 38, 167–176 (2024).
Google Scholar
Yang, X. et al. Utilizing electronic health record data to understand comorbidity burden among people living with HIV: a machine learning approach. AIDS 35, S39–S51 (2021).
Google Scholar
González-Prieto, Á, Brú, A., Nuño, J. C. & González-Álvarez, J. L. Hybrid machine learning methods for risk assessment in gender-based crime. Knowl. Based Syst. 260, 110130 (2023).
Google Scholar
McDougal, L. et al. Opening closed doors: using machine learning to explore factors associated with marital sexual violence in a cross-sectional study from India. BMJ Open 11, e053603 (2021).
Google Scholar
Silva, M. et al. Gender-based violence narratives in internet-based conversations in Nigeria: social listening study. J. Med. Internet. Res. 25, e46814 (2023).
Google Scholar
Orts Llopis, M. Á. Las leyes sobre la vioLencia de género y doméstica en España y Reino Unido y la emoción: un estUdio léxico deL discUrso jUrídico desde eL anáLisis deL sentimiento. Rev. Llen. Dret 71, 171–192 (2019).
Udomboso, C. G. & Amoateng, A. Modelling trends in contraception usage in Nigeria and Ghana. J. Health Manag. 20, 277–290 (2018).
Google Scholar
Liew, T. W., Tan, S.-M., Yoo, N. E., Gan, C. L. & Lee, Y. Y. Let’s talk about Sex!: AI and relational factors in the adoption of a chatbot conveying sexual and reproductive health information. Comput. Hum. Behav. Rep. 11, 100323 (2023).
Google Scholar
Nadarzynski, T., Bayley, J., Llewellyn, C., Kidsley, S. & Graham, C. A. Acceptability of artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled chatbots, video consultations and live webchats as online platforms for sexual health advice. BMJ Sex. Reprod. Health 46, 210–217 (2020).
Google Scholar
Stevens, R. et al. On sex, drugs, and alcohol: a mixed-method analysis of youth posts on social media in the United States. J. Child. Media 16, 514–531 (2022).
Google Scholar
Selskyy, P., Sverstiuk, A., Slyva, A. & Selskyi, B. Prediction of the progression of endometrial hyperplasia in women of premenopausal and menopausal age based on an analysis of clinical and anamnestic indicators using multiparametric neural network clustering. Fam. Med. Prim. Care Rev. 25, 184–189 (2023).
Thawnashom, K., Pornsawad, P. & Makond, B. Machine learning’s performance in classifying postmenopausal osteoporosis Thai patients. Intell. Based Med. 7, 100099 (2023).
Google Scholar
Zeitlin, J., Parides, M. K., Lane, J. M., Russell, L. A. & Kunze, K. N. A clinical prediction model for 10-year risk of self-reported osteoporosis diagnosis in pre-and perimenopausal women. Arch. Osteoporos. 18, 78 (2023).
Google Scholar
Chao, Q. et al. Menopausal women’s health care method based on computer nursing diagnosis intelligent system. J. Healthc. Eng. 2021, 4963361 (2021).
Google Scholar
Swanson, K. et al. Effect of recent abortion legislation on Twitter user engagement, sentiment, and expressions of trust in clinicians and privacy of health information: content analysis. J. Med. Internet. Res. 25, e46655 (2023).
Google Scholar
Ujah, O. I., Olaore, P., Nnorom, O. C., Ogbu, C. E. & Kirby, R. S. Examining ethno-racial attitudes of the public in Twitter discourses related to the United States Supreme Court Dobbs vs. Jackson Women’s Health Organization ruling: a machine learning approach. Front. Global Women’s Health. (2023).
Valdez, D., Jozkowski, K. N., Montenegro, M. S., Crawford, B. L. & Jackson, F. Identifying accurate pro-choice and pro-life identity labels in Spanish: social media insights and implications for comparative survey research. Perspect. Sex. Reprod. Health 54, 166–176 (2022).
Google Scholar
Alabi, O. et al. Robust fetoscopic mosaicking from deep learned flow fields. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 17, 1125–1134 (2022).
Google Scholar
Płotka, S. S. et al. Deep learning for estimation of fetal weight throughout the pregnancy from fetal abdominal ultrasound. Am. J. Obstetr. Gynecol. MFM. (2023).
Shahzad, S. et al. Sperm abnormality detection using sequential deep neural network. Mathematics 11, 515 (2023).
Google Scholar
Xia, T.-H. et al. Establish a normal fetal lung gestational age grading model and explore the potential value of deep learning algorithms in fetal lung maturity evaluation. Chin. Med. J. 134, 1828–1837 (2021).
Google Scholar
Yeo, L. & Romero, R. Fetal Intelligent Navigation Echocardiography (FINE): a novel method for rapid, simple, and automatic examination of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 42, 268–284 (2013).
Google Scholar
Hariton, E. et al. A machine learning algorithm can optimize the day of trigger to improve in vitro fertilization outcomes. Fertil. Steril. 116, 1227–1235 (2021).
Google Scholar
Letterie, G. & Mac Donald, A. Artificial intelligence in in vitro fertilization: a computer decision support system for day-to-day management of ovarian stimulation during in vitro fertilization. Fertil. Steril. 114, 1026–1031 (2020).
Google Scholar
Mirroshandel, S. A., Ghasemian, F. & Monji-Azad, S. Applying data mining techniques for increasing implantation rate by selecting best sperms for intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection treatment. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 137, 215–229 (2016).
Google Scholar
Wang, Y. et al. Task model-specific operator skill assessment in routine fetal ultrasound scanning. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 17, 1437–1444 (2022).
Google Scholar
Guh, R.-S., Wu, T.-C. J. & Weng, S.-P. Integrating genetic algorithm and decision tree learning for assistance in predicting in vitro fertilization outcomes. Expert Syst. Appl. 38, 4437–4449 (2011).
Google Scholar
Lu, H., Hirst, J., Yang, J., Mackillop, L. & Clifton, D. Standardising the assessment of caesarean birth using an Oxford caesarean prediction score for mothers with gestational diabetes. Health. Technol. Lett. 9, 1–8 (2022).
Google Scholar
Ekpenyong, M. E., Etebong, P. I. & Jackson, T. C. Fuzzy-multidimensional deep learning for efficient prediction of patient response to antiretroviral therapy. Heliyon 5, e02080 (2019).
Bulka, C. M. et al. Arsenic in private well water and birth outcomes in the United States. Environ. Int. 163, 107176 (2022).
Google Scholar
Klein, A. Z., Sarker, A., Weissenbacher, D. & Gonzalez-Hernandez, G. Towards scaling Twitter for digital epidemiology of birth defects. NPJ Digit. Med. 2, 96 (2019).
Google Scholar
Ailes, E. C. et al. Using supervised learning methods to develop a list of prescription medications of greatest concern during pregnancy. Matern. Child Health J. 24, 901–910 (2020).
Google Scholar
Ghasemi, G. & Nemati-Rashtehroodi, A. QSAR modeling of benzimidazole derivatives as potent inhibitors of trichomoniasis/QSAR modellemesi ile Benzimidazole türevlerinin trikomoniasis için etkili inhibitörler olarak kullanılması. Turkish J. Biochem. 40, 492–499 (2015).
Google Scholar
Kang, L. et al. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) model for predicting teratogenic risk of antiseizure medications in pregnancy by using support vector machine. Front Pharm. 13, 747935 (2022).
Google Scholar
Bickmore, T., Zhang, Z., Reichert, M., Julce, C. & Jack, B. Promotion of preconception care among adolescents and young adults by conversational agent. J. Adolesc. Health 67, S45–S51 (2020).
Google Scholar
Chervenak, J., Lieman, H., Blanco-Breindel, M. & Jindal, S. The promise and peril of using a large language model to obtain clinical information: ChatGPT performs strongly as a fertility counseling tool with limitations. Fertil. Steril. 120, 575–583 (2023).
Google Scholar
Qin, M., Xu, Y., Liang, Y. & Sun, T. A wearable fetal movement detection system for pregnant women. Front. Med. 10, 1160373 (2023).
Google Scholar
Jennings, V., Haile, L. T., Simmons, R. G., Spieler, J. & Shattuck, D. Perfect-and typical-use effectiveness of the Dot fertility app over 13 cycles: results from a prospective contraceptive effectiveness trial. Eur. J. Contracept. Reprod. Health Care 24, 148–153 (2019).
Google Scholar
Sexual and reproductive health interventions in the WHO UHC Compendium https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240022867.
Haugen, T. B. et al. Sperm motility assessed by deep convolutional neural networks into WHO categories. Sci. Rep. 13, 14777 (2023).
Google Scholar
Gunderson, S. J. et al. Machine-learning algorithm incorporating capacitated sperm intracellular pH predicts conventional in vitro fertilization success in normospermic patients. Fertil. Steril. 115, 930–939 (2021).
Google Scholar
Merz, A. A. et al. Population attitudes toward contraceptive methods over time on a social media platform. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 224, 597.e591–597.e514 (2021).
Google Scholar
Du, J. et al. Use of deep learning to analyze social media discussions about the human papillomavirus vaccine. JAMA Netw. Open 3, e2022025 (2020).
Google Scholar
Movaghar, A., Mailick, M., Sterling, A., Greenberg, J. & Saha, K. Automated screening for Fragile X premutation carriers based on linguistic and cognitive computational phenotypes. Sci. Rep. 7, 2674 (2017).
Google Scholar
Shara, N. et al. Early identification of maternal cardiovascular risk through sourcing and preparing electronic health record data: machine learning study. JMIR Med. Inform. 10, e34932 (2022).
Google Scholar
Klein, A. Z. & Gonzalez-Hernandez, G. An annotated data set for identifying women reporting adverse pregnancy outcomes on Twitter. Data Brief. 32, 106249 (2020).
Google Scholar
Rigla, M., Martínez-Sarriegui, I., García-Sáez, G., Pons, B. & Hernando, M. E. Gestational diabetes management using smart mobile telemedicine. J. Diab. Sci. Technol. 12, 260–264 (2018).
Google Scholar
Kim, T. The impact of working hours on pregnancy intention in childbearing-age women in Korea, the country with the world’s lowest fertility rate. PLoS ONE 18, e0288697 (2023).
Google Scholar
Day, T. G. et al. Prenatal diagnosis of hypoplastic left heart syndrome on ultrasound using artificial intelligence: how does performance compare to a current screening programme?. Prenat. Diagn. 44, 717–724 (2024).
Google Scholar
Wang, F., Mao, R., Yan, L., Ling, S. & Cai, Z. A deep learning-based approach for rectus abdominis segmentation and distance measurement in ultrasonography. Front Physiol. 14, 1246994 (2023).
Google Scholar
Marcus, J. L. et al. Use of electronic health record data and machine learning to identify candidates for HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis: a modelling study. Lancet HIV 6, e688–e695 (2019).
Google Scholar
MacDowell, M. et al. Understanding birthing mode decision making using artificial neural networks. Med Decis. Mak. 21, 433–443 (2001).
Google Scholar
Zhao, M. et al. Identification and immuno-infiltration analysis of cuproptosis regulators in human spermatogenic dysfunction. Front. Genet. 14, 1115669 (2023).
Google Scholar
Candemir, C. Estimating the semen quality from life style using fuzzy radial basis functions. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Comput. 8, 44–48 (2018).
Google Scholar
Fraiwan, L. et al. Time frequency analysis for automated sleep stage identification in fullterm and preterm neonates. J. Med. Syst. 35, 693–702 (2011).
Google Scholar
Sadda, P. et al. Deep-learned placental vessel segmentation for intraoperative video enhancement in fetoscopic surgery. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 14, 227–235 (2019).
Google Scholar
Stockman, J., Friedman, J., Sundberg, J., Harris, E. & Bailey, L. Predictive analytics using machine learning to identify ART clients at health system level at greatest risk of treatment interruption in Mozambique and Nigeria. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 90, 154–160 (2022).
Google Scholar
Das, R. et al. Performance analysis of machine learning algorithms and screening formulae for β-thalassemia trait screening of Indian antenatal women. Int. J. Med. Inf. 167, 104866 (2022).
Google Scholar
Katebi, N., Sameni, R., Rohloff, P. & Clifford, G. D. Hierarchical attentive network for gestational age estimation in low-resource settings. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inf. 27, 2501–2511 (2023).
Google Scholar
Kulkarni, S. S., Katebi, N., Valderrama, C. E., Rohloff, P. & Clifford, G. D. CNN-based LCD transcription of blood pressure from a mobile phone camera. Front Artif. Intell. 4, 543176 (2021).
Google Scholar
Schilpzand, M. et al. Automatic placenta localization from ultrasound imaging in a resource-limited setting using a predefined ultrasound acquisition protocol and deep learning. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 48, 663–674 (2022).
Google Scholar
Simplified models to assess newborn gestational age in low-middle income countries: findings from a multicountry, prospective cohort study. BMJ Glob Health. (2021).
Revell, A. D. et al. An update to the HIV-TRePS system: the development of new computational models that do not require a genotype to predict HIV treatment outcomes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 69, 1104–1110 (2014).
Google Scholar
Gomes, R. G. et al. A mobile-optimized artificial intelligence system for gestational age and fetal malpresentation assessment. Commun. Med. 2, 128 (2022).
Google Scholar
Revell, A. D. et al. 2021 update to HIV-TRePS: a highly flexible and accurate system for the prediction of treatment response from incomplete baseline information in different healthcare settings. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 76, 1898–1906 (2021).
Google Scholar
Holmström, O. et al. Point-of-care digital cytology with artificial intelligence for cervical cancer screening in a resource-limited setting. JAMA Netw. Open 4, e211740 (2021).
Google Scholar
Jaganath, D. et al. Evaluation of multi-antigen serological screening for active tuberculosis among people living with HIV. PLoS ONE 15, e0234130 (2020).
Google Scholar
Kebede, S. D. et al. Prediction of contraceptive discontinuation among reproductive-age women in Ethiopia using Ethiopian Demographic and Health Survey 2016 Dataset: a Machine Learning Approach. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 23, 9 (2023).
Google Scholar
Togunwa, T. O., Babatunde, A. O. & Abdullah, K. -u-R. Deep hybrid model for maternal health risk classification in pregnancy: synergy of ANN and random forest. Front. Artif. Intell. 6, 1213436 (2023).
Google Scholar
Rittenhouse, K. J. et al. Improving preterm newborn identification in low-resource settings with machine learning. PLoS ONE 14, e0198919 (2019).
Google Scholar
Bahado-Singh, R. et al. Cell-free DNA in maternal blood and artificial intelligence: accurate prenatal detection of fetal congenital heart defects. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 228, 76.e71–76.e10 (2023).
Google Scholar
Dabi, Y. et al. Endometriosis-associated infertility diagnosis based on saliva microRNA signatures. Reprod. Biomed. online 46, 138–149 (2023).
Google Scholar
Sivasankaran, S. & Jonnalagadda, S. Levonorgestrel loaded biodegradable microparticles for injectable contraception: preparation, characterization and modelling of drug release. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 624, 121994 (2022).
Google Scholar
Fan, Z. et al. CAM-VT: A weakly supervised cervical cancer nest image identification approach using conjugated attention mechanism and visual transformer. Comput. Biol. Med. 162, 107070 (2023).
Google Scholar
Lin, Q. & Fang, Z.-J. Establishment and evaluation of a risk prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus. World J. Diab. 14, 1541 (2023).
Google Scholar
Alowais, S. A. et al. Revolutionizing healthcare: the role of artificial intelligence in clinical practice. BMC Med. Educ. 23, 689 (2023).
Google Scholar
Russell, S. J. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach. Third edition edn (Prentice Hall, 2010).
Masilamani, V. et al. Leveraging artificial intelligence for advancements in reproductive health. Afr. J. Reprod. Health 28, 216–217 (2024).
Google Scholar
Cruz Rivera, S., Liu, X., Chan, A. W., Denniston, A. K. & Calvert, M. J. Guidelines for clinical trial protocols for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the SPIRIT-AI extension. Lancet Digit. Health 2, e549–e560 (2020).
Google Scholar
Liu, X., Cruz Rivera, S., Moher, D., Calvert, M. J. & Denniston, A. K. Reporting guidelines for clinical trial reports for interventions involving artificial intelligence: the CONSORT-AI extension. Nat. Med. 26, 1364–1374 (2020).
Google Scholar
Arksey, H. & O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 8, 19–32 (2005).
Google Scholar
Tamrat, T. et al. Exploring the use and implications of AI in sexual and reproductive health and rights: protocol for a scoping review. JMIR Res. Protoc. 13, e53888 (2024).
Google Scholar
Fox, M. P., Lash, T. L. & Bodnar, L. M. Common misconceptions about validation studies. Int J. Epidemiol. 49, 1392–1396 (2020).
Google Scholar
Carlson, M. D. & Morrison, R. S. Study design, precision, and validity in observational studies. J. Palliat. Med 12, 77–82 (2009).
Google Scholar
Rubinger, L., Gazendam, A., Ekhtiari, S. & Bhandari, M. Machine learning and artificial intelligence in research and healthcare. Injury 54, S69–S73 (2023).
Google Scholar
World Health Organization. Monitoring and Evaluating Digital Health Interventions: A Practical Guide to Conducting Research and Assessment (World Health Organization, 2016).
Zhang, C., Fan, C., Yao, W., Hu, X. & Mostafavi, A. Social media for intelligent public information and warning in disasters: an interdisciplinary review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 49, 190–207 (2019).
Barbounaki, S. G., Gourounti, K. & Sarantaki, A. Advances of sentiment analysis applications in obstetrics/gynecology and midwifery. Mater. Sociomed. 33, 225–230 (2021).
Google Scholar
World Health Organization. Classification of Digital Interventions, Services and Applications in Health: A Shared Language to Describe the Uses of Digital Technology for Health, 2nd edn (World Health Organization, 2023).
Metreau, E., Young, K. & Eapen, S. World Bank country classifications by income level for 2024–2025. World Bank Blogs. (2024).
Ng, M. Y., Kapur, S., Blizinsky, K. D. & Hernandez-Boussard, T. The AI life cycle: a holistic approach to creating ethical AI for health decisions. Nat. Med. 28, 2247–2249 (2022).
Google Scholar
link